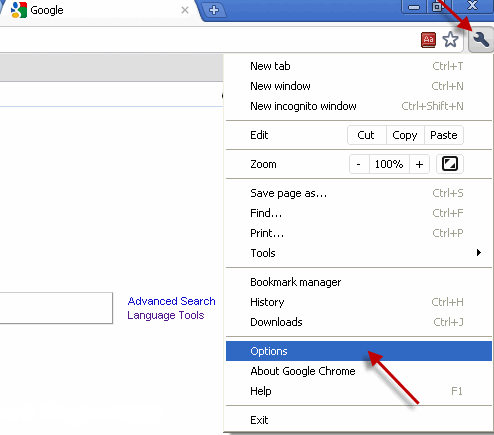
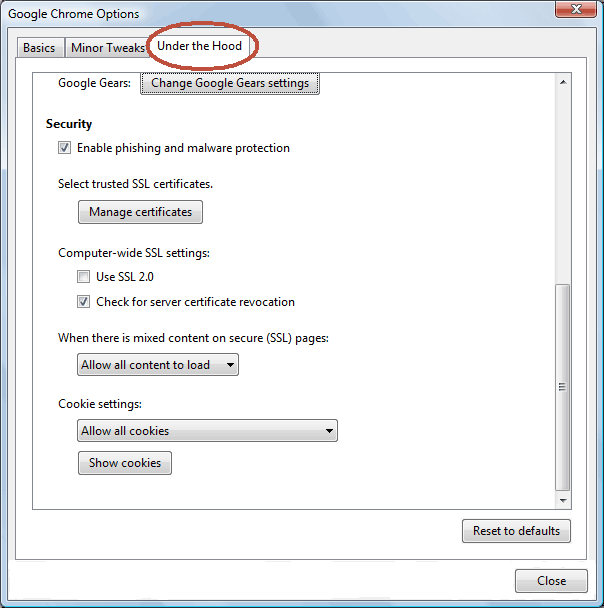
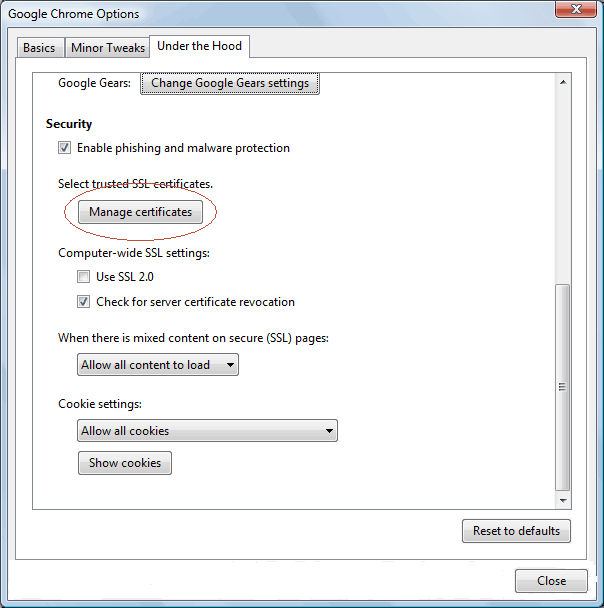
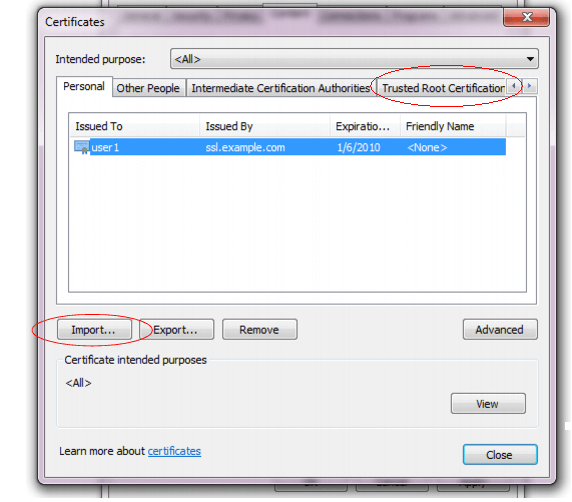
The Norton Secured Site seal is no longer offered starting Oct. 16, 2023.
Tips to Choose The Best Certificate Authority (CA)

Over the years, as the arena of e-commerce flourished, the SSL industry as well, expanded along with it. So much so, that it is now impossible to imagine a safe and successful e-commerce website without an SSL certificate safeguarding it. Whether it’s the new best-seller you are buying from amazon.com or accessing your bank account online, an SSL certificate is always there to safeguard the information you submit online. Just as important as SSLs are the Certificate Authorities (CAs), a trusted third party organization that issues digital certificates. Their duty is to authenticate the identities of the two parties exchanging information. That is the reason all the CAs hold significant importance in data security and e-commerce industry.
This extensive usage of SSL certificates have given way to CAs to come up with SSL certificates with myriad features and characteristics. In fact, the website owners now have too many options to choose from when it comes to zeroing down on an SSL certificate as per the website requirement and a Certificate Authority (CA) issuing one. There are many factors like costing, features etc which need to be considered before choosing an SSL certificate and a CA. Here, we help you get acquainted with few of the major names in the CA industry: Symantec, GeoTrust, Thawte and RapidSSL.
Symantec

Symantec was established in the year 1992, since then it has evolved to become one of the leading SSL certificates’ suppliers across the world. Operating in more than 50 countries across the world, Symantec today houses around 18,500 employees. They are good at providing online security, storage and systems management solutions to support their customers who range from online consumers and small scale businesses to large global organizations. Symantec helps them secure and manage their online businesses.
Why Symantec
Many organizations and e-commerce merchants have chosen Symantec to be their first choice for SSL certificates. Here, we put together few reasons for you to have a look at:
- Outstanding Online Customer Support: Prompt 24/7 customer service is complemented by Express Renewal and 30-day money back guarantee
- Norton Secured Seal: This seal is the most trusted mark on the Internet and is viewed more than half a billion times per day across 170 countries. Symantec’s Seal-In-Search displays Norton Secured Seal next to the links
- More than a Digital Certificate: It helps drive traffic to the website and reduce abandoned transactions. Its features like Norton Security Seal, Search-In-Seal technology work in sync to assure customers that the site is safe and secured.
- Malware Scanning: Symantec SSL certificate protects your website from malware by performing daily website malware scanning
Products
| Product Name |
Issuance Time |
Validation |
Site Seal |
| Secure Site Pro with EV |
5 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Secure Site with EV |
5 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Secure Site Pro |
2 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Secure Site |
4-5 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Code Signing Certificate |
2-3 Days |
Organization |
N/A |
| Symantec Safe Site |
2-3 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Symantec Secure Site Wildcard |
1-2 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
Site Seal Importance
Symantec’s Norton Secured Seal is the most trusted mark on the Internet. It is viewed half a billion times per day across about 170 countries. It enables you to grow more traffic and maximize web sales by letting the visitors know that they are browsing and buying from a secured site. More than 40 million desktops using Norton Safe Web across the world see Norton Secured Seal next the trusted websites in the search results.
GeoTrust

Established in 2001, GeoTrust is headquartered in California, US. GeoTrust is world’s second largest digital certificate provider. Previously owned by VeriSign, today GeoTrust is owned by Symantec. More than 100,000 customers across 150 countries rely on GeoTrust to secure their online transactions and websites. Digital certificates and trust products by GeoTrust enable businesses and organizations maximize the security of any web-based transactions at cost-effective rates.
Why GeoTrust
- Quick Turnaround Time: GeoTrust helps you get an SSL certificate in real time. One can even use, manage and renew an SSL very conveniently.
- Cost-efficient: GeoTrust have a wide range of excellent quality certificates that are sold at market-low prices. Also the SAN-enabled certificates offer inexpensive and flexible multi-domain options.
- Unlimited Server Licensing: A single certificate can secure an unlimited number of servers. Re-issuing is free of cost as well.
- Diverse Options: GeoTrust houses a variety of SSL certificates that range from simple domain-validated certificates to business-boosting Extended Validated certificates with green address bar.
Products
| Product Name |
Issuance Time |
Validation |
Site Seal |
| GeoTrust QuickSSL Premium SSL |
10 Minutes |
Domain |
Dynamic |
| GeoTrust True Business ID with EV |
1 to 10 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| GeoTrust True Business ID |
2 to 4 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| GeoTrust True BusinessID Multi Domain (SAN/UCC) |
1 to 2 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| GeoTrust BusinessID Wildcard SSL |
1 to 2 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Symantec Safe Site |
2-3 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| GeoTrust True BusinessID with EV Multi Domain |
1 to 10 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Geo-Trust Web Site Anti-Malware Scan |
N/A |
Domain |
N/A |
Site Seal Importance
Customers’ anxieties and concerns tend to heighten as they submit their personal or financial information on websites. But in case of GeoTrust, all these concerns are put to rest by an assuring symbol of GeoTrust Site seal pasted on the web page. It acts like an instant proof for your customers that they are visiting a website that has a stamp of approval by leading Certificate Authorities for safe e-transactions.
It’s advisable to add these Site Seals to your home page, payment page and other such pages of website where visitors need to verify the website’s authenticity.
Thawte

Established in the year 1995 by Mark Shuttleworth in South Africa, Thawte has quickly grown into one of the most trusted Certificate Authorities. In fact, it was the first Certificate Authority to issue SSL certificates to public entities outside the US. Till date, Thawte has issued more than 945, 000 SSL certificates and code signing certificate across 240 countries.
Thawte was acquired by VeriSign in the year 2000 and continues to prosper as a separate brand. Popular among the small businesses throughout Europe and Asia, Thawte is also chosen by millions across the world for securing their web pages.
Why Thawte
- It accounts for about 40% of global market
- First to provide multi-lingual trust seals, which builds confidence in customers by verifying
- Enables more people to navigate the web safely on their own
- Advanced SSL protection that includes rigorous authentication process and strong infrastructure
Products
| Product Name |
Issuance Time |
Validation |
Site Seal |
| Thawte SSL Web Server with EV |
1 to 10 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Thawte SSL 123 |
10 Minutes |
Domain |
Dynamic |
| Thawte SSL Web Server |
1 to 2 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Thawte SGC SuperCerts |
1 to 10 Days |
Organization |
Dynamic |
| Thawte Wildcard SSL Certificate |
1 to 2 Days |
Organization |
N/A |
| Thawte Code Signing Certificate |
2-3 Days |
Organization |
N/A |
| Thawte Code Signing Individual |
2-3 Days |
Organization |
N/A |
Site Seal Importance
Thawte was the first one to come up with the concept of a Multi-Lingual Site Seal which is now available in about 18 different local languages. They provide visual reassurance that Thawte has verified the site’s identity and that it’s safe to carry out transactions on that site as they are secured by SSL. The seal is displayed within 2 hours of installing.
On clicking the Trusted Seal on web pages, a seal verification page opens in a new browser window and shows the verified domain name; certificate authority that performed the authentication; and the validity period. In case of full organization validation and Extended Validation, the SSL certificate also displays the organization’s name and location.
Thawte recommends adding the seal script to secured home page, buy page, sign-in page, and all other pages in your secured domain where customers need assurance.
RapidSSL

SSL certificates by RapidSSL are an apt choice to secure small and medium sized businesses and web pages having limited traffic. RapidSSL is owned and operated by GeoTrust, Inc and is focused on providing websites of small/medium enterprises or businesses (SME) with strong protection of 128/256 bit.
RapidSSL certificates are Domain Validated (DV) and issued within few minutes. Their economical range of SSL certificates is very advantageous to SME e-commerce businesses. Their root certificates are compatible with 99% of browsers. A static trust mark of RapidSSL’s site seal is provided that can be displayed on the website along with other display cues like https URL and a closed padlock icon.
Why RapidSSL
RapidSSL’s inexpensive range of SSL certificates happens to be the principle reason behind it being chosen over other brands, especially by small and medium e-commerce websites. There are several other reasons as well which can be listed down as follows:
- Complete automated validation
- Root certificate has 99$ browser recognition
- Strong 256-bit encryption
Products
| Product Name |
Issuance Time |
Validation |
Site Seal |
| RapidSSL Certificates |
Immediate |
Domain |
Static |
| Rapid SSL Wildcard |
Immediate |
Domain |
Static |
| Free Rapid SSL |
10-15 minutes |
Domain |
Static |
Site Seal Importance
RapidSSL offers all its clients to display a Site Seal on its (client’s) website. A website seal is of great importance as it ensures website trust and establishes credibility to all the potential customers visiting the website. RapidSSL decided to release an updated version of its logo in the year 2011. It’s a GIF with rotating display of ‘Secured by RapidSSL’, its encryption strength and warranty. This is an entry level certificate that would provide basic validation and authentication of your website. This certificate is perfect for you if you are looking to set up basic web presence and need an SSL certificate right away.
Conclusion
And so, choosing a Certificate Authority can get a bit confusing as there are too many factors involved that are to be taken into consideration. But ultimately the CA you end up choosing has to have the framework, product range and costing that perfectly fit websites’ security needs and your budget at the same time.